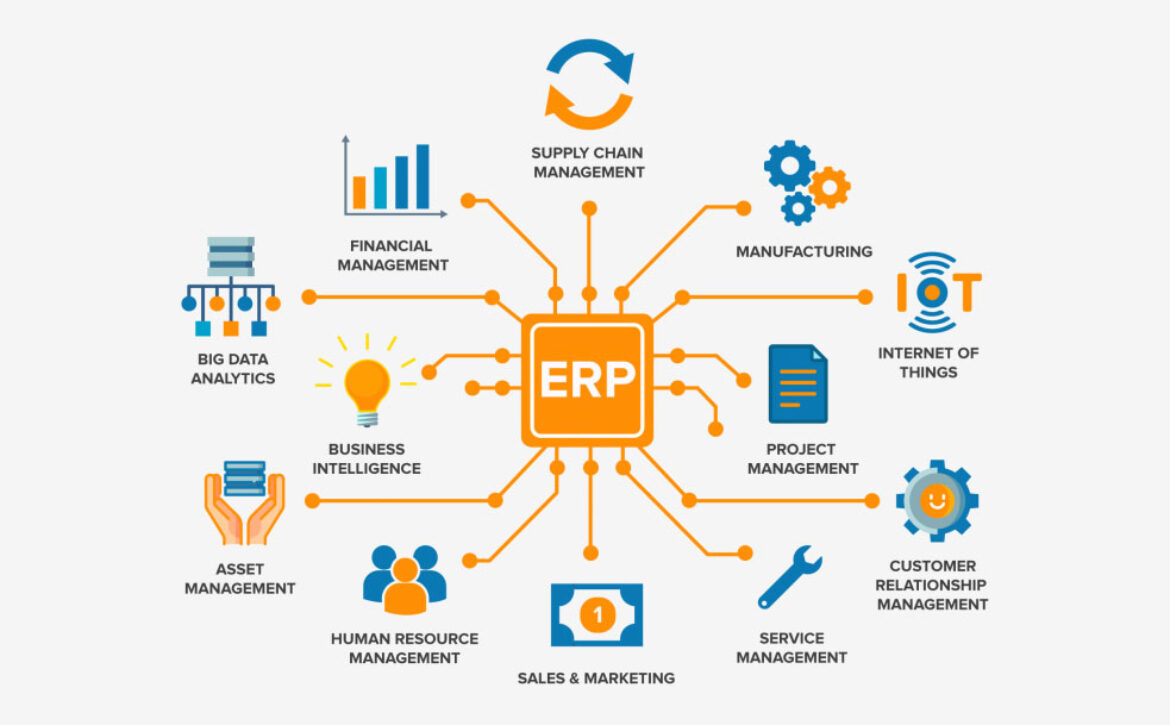
Get a detailed comparison of the architecture, performance, testing, mobile app size, and user experience of Flutter and React Native. Choose the one that is best for your project as well.
The development sector has been severely impacted by the growth of mobile applications. With more than 3.6 billion mobile users worldwide, new methods are making it quicker and easier to create mobile apps. The two main hybrid frameworks for creating mobile apps are Flutter and React Native. And their respective followings are growing.
However, the majority of businesses believe that creating native apps for each device is a massive time waster. They look for specialized technologies to build cross-platform mobile applications and debate between Flutter and React Native as to which is better.
So why would we choose to create native applications when hybrid ones are an option? The two ideal cross-platform development solutions are Flutter and React Native. Both provide a wide range of features, open-source frameworks, and the ability to build almost any kind of application.
Although Flutter and React Native have two similar aspects of cross-platform app development, they are sometimes considered to be bitter rivals. Both assist developers in lowering the Time to Market (TTM) for providing clients with engaging business apps, boosting productivity.
To assist their clients in growing their businesses, many mobile app development companies create world-class apps using the best-in-fit methodology. This post will emphasize employing a more defined strategy as an alternative to using a particular technology framework, such as native, React Native, or Flutter.
Here, we contrast React Native with Flutter in order to clarify their key distinctions and assist decision-makers in choosing the appropriate tech stack.
Let’s first dive in to learn a fundamental overview to Flutter and React Native as we start a thorough comparison.
The Flutter cross-platform ui framework was developed by Google. Since Flutter’s original release in May 2017, its popularity has continuously increased.
One of the main selling points for Flutter is its ability to construct cross-platform apps from a single codebase. In the past, creating an application that could be used on desktop, mobile, and the web required a number of technologies and developers.
For instance, you might need:
- The website was created using React by a web developer that specializes in that field.
- C# and Java was used by other developers to produce the desktop version.
- An expert mobile developer uses Swift and Kotlin to create Android and iOS apps.
In order to make sure that the Flutter app design and branding are consistent throughout all platforms, this strategy would need a sizable engineering team and numerous meetings. Other factors include testing each system and resolving any faults or idiosyncrasies it may have.
Businesses must maintain a single codebase while creating apps for numerous platforms using Flutter app development. The time and money required to create and maintain an application are drastically reduced.
Flutter 3 brought about a number of important modifications. Despite the fact that the API for creating mobile and web applications doesn’t vary significantly, the Flutter Compiler enables you to create apps for the iPhone, Android, Web, Windows, Mac, and Linux using a single codebase.
For those who want to utilize it to create a game, Flutter 3 also has improved Firebase compatibility and a Casual Games Toolkit.
These surprising figures about Flutter market usage will astound you:
- Flutter is used by 42% of individuals worldwide to create cross-platform mobile applications. (Data from Statista)
- Flutter is adored by 68.8% of the growing community. (Referring to StackOverflow)
- The choice of 13.55% of the community was Flutter, which is well-liked for its libraries and tools. (Referring to StackOverflow)
The cross-platform React Native framework was created by Facebook. By making it very simple to create cross-platform applications utilizing a JavaScript codebase, React Native lowers the access for JavaScript developers.
Most web developers use JavaScript since it has been for a while and is useful for their projects. Though the ecosystem for React Native app creation is still young, it has expanded significantly in recent years.
If you are already familiar with JavaScript, learning how to create mobile apps with React Native won’t be as difficult.
Nowadays, React Native is widely used in the app development industry. The new Xbox store application is one competitive edge that Microsoft has recently developed with React Native. Similar to Flutter, React Native enables the creation of cross-platform applications using a single codebase.
The recently released React Native architecture, which makes use of the TurboModule and Fabric Renderer systems, is enabled by the edition of React Native 0.68, which allows opt-in support. Because not all libraries have switched over to the new architecture yet, it is just opt-in.
The Fabric Renderer enhances React Native by bringing React Suspense, concurrency, and server-side rendering with a quicker and more adaptable toolbox.
These astounding numbers about the expansion of the React Native market:
- In 2021, 38% of developers created cross-platform applications using React Native. (Data from Statista)
- Due to its native tools and libraries, React Native is preferred by 14.51% of developers. (Referring to StackOverflow)
- React Native is beloved by 58.8% of the developer industry. (Referring to StackOverflow)
Hot-reloading: The programme is updated instantly without losing its state thanks to the Stateful Hot Reloading capability.
Rich widgets: Offers rich widgets compliant with Cupertino and Material Design (Android) standards (iOS).
Seamless integration: There is no need to modify any code because it links with Java for Android and Swift or Objective C for iOS with ease.
Quick shipping: Because just one codebase needs to be tested, it allows for quick iteration cycles and cuts down on build time.
Codesharing: It is perfect for MVP development because it enables faster and easier writing and sharing of codes across platforms.
Tools and Plugins: React Native has more resources, despite the fact that the libraries and tools are excellent.
User interface: Plugins struggle to quickly support vector graphics and animation.
Operating system: Unsuitable for watchOS, CarPlay, Android Auto, or tvOS app development.
Updates: Without initially going through the standard release steps, patches and updates cannot be quickly deployed into apps.
Native Rendering: Renders APIs directly on the host platform without the use of HTML or CSS markup.
Performance: Maintains excellent performance while converting an application’s HTML to imitate UI components.
Ecosystem: Redraws the app’s design anytime a state changes using a strong ecosystem and UI frameworks.
Debugging: Error reporting and intelligent debugging tools are made available through debugging.
Hot reloading: This technique allows for the immediate insertion of fresh codes into applications that are already executing.
Tools and plugins: Third-party libraries that are used for better implementation are often out-of-date.
Performance: Because parallel thread and multiple processing are not supported, it performs poorly.
Debugging: When debugging, it may be difficult to alter, examine codes, and correctly display UI elements.
How React Native and Flutter operate differently is up for debate. Since everything about Flutter and React Native points to their being speedy and nimble, the “performance” debate in their respective communities is a little contentious. React Native has also been honed for its performance because native modules and outside libraries are used. Let’s delve further to learn more about how Flutter and React Native operate differently.
A Flutter app operates more quickly than a React Native one. There is no requirement for a bridge to enable interaction between native modules because the native components are crucially available. The “hello world” software consistently generated pictures at 60 frames per second, and it took less than 16 milliseconds for each frame to appear, according to the performance test. There were less dropped frames, which is positive. As was already mentioned, Flutter makes use of the Skia graphics package, allowing the user interface to be changed each time the application view changes. It makes sense that Flutter can function well even at 60 frames per second.
React Native performs worse than Flutter, and this is because of the JavaScript bridge that links native modules. When compared to a Flutter “Hello World” app, a React Native “hello world” app far more frequently drops frames. When rendering a code, the application occasionally stutters if it takes more than 16 milliseconds. You can speed up your programme by using third-party libraries like Proguard, which optimizes bytecodes. Furthermore, tools like Slowlog help set performance timers that may be used to monitor and resolve performance issues.
A number of structural advantages are offered to application developers by both Flutter and React Native. Let’s talk about them in more depth.
Layers make up Flutter’s structure. This framework’s top-level root function, or in other words, platform-specific widgets, serves as the foundation of the architecture of a fundamental application. The following are basic widgets that interact with the platform and rendering layers. Above the rendering layer are the animation movements that represent API calls to the application’s base layer. It also goes by the name Scaffold and is powered by a C/C++ engine and a platform-specific embedder.
If you want to separate the display layer from business logic, think about using Flutter BLoC. This architecture makes it easier for both expert and novice Flutter developers to develop big apps from small, accessible components.
The Native thread and JavaScript thread are connected internally by React Native. Through this capability, the JavaScript code interacts with the platform and the Native API. Instead of using JavaScriptCore separately to run all programmes on iOS, React Native integrates into the Android application. Although this could enhance native functionality, it also makes the app larger, which could affect performance or device latency.
Maintaining faultless code execution with the least amount of time and effort is one of the key goals of development. In the section below, we’ll examine how much easier testing is in Flutter and React Native apps.
Flutter uses a dart to operate, which offers a lot of help for automated testing. It has thorough documentation and a variety of testing tools for unit, widget, and integration testing of applications. The deployment process is completely documented, and Flutter also provides comprehensive instructions for creating and releasing iOS apps on the Apple Play Store and Google Play Store.
UI-level testing and integration testing are not officially supported, boasting React Native. Furthermore, there aren’t many frameworks available for unit evaluating React Native applications. Developers must rely on third-party tools like Appium and Detox to detect issues because there isn’t any official support.
Additionally, it continues to use third-party libraries to automate release and development. The entire framework does not include any automated methods for publishing iOS apps to the App Store. React Native suggests that developers utilize Xcode to define the manual app deployment process instead.
User experience is crucial while choosing the best mobile development framework for any project. It seeks to offer simple experiences that motivate customers to stick with the company or product. You can specify customer journeys on the website that are most advantageous to business growth thanks to a meaningful user experience.
Flutter offers a great user experience by utilizing simplified tools, features, and unique widgets. A generational garbage collection feature in Dart makes it easier to create UI frames for potentially transient object codes. Dart’s capability avoids UI clutter, garbage, and shutter of animation delay while the programme is being built by allocating objects within a single pointer bump.
Ability of React Native to deliver the most amazing user experience
React Native finds it difficult to maintain consistency with the needs of native platforms, such as iOS’ Style Design and Android’s Material Design, which are always changing. Additionally, because of premade UI kits like React Virgin, Ant Design, and Shoutem, it is significantly more difficult to create uniform designs across platforms. The UX is significantly improved across many platforms by a number of crucial components, including the ScrollView fixed header, the Activity indicators, the Snap carousels, and the Pagination components.
The choice of a mobile framework may have a considerable impact on the size of the application code, therefore for a large project, the application size should be more than the framework size. Less size is always more in this circumstance. Compare the application sizes created by Flutter versus React Native.
A simple hello world Flutter app is about 7.5 MB in size. The C/C++ engine and Dart Virtual Machine have an impact on the size of Flutter apps. Flutter may self-contain all programmes and assets to avoid size problems. A particular tag like -split-debug-info can be included to reduce the size of the code.
The initial size of the Hello World React Native app was 7 MB. Later, native dependencies were added, and the size increased to 13.4 MB. React Native can iterate projects more quickly and with less file sizes than Flutter.
When Proguard is enabled and the enabled SeparateBuild Per CPU Architecture element is utilized, it will further decrease the size by automatically producing split builds for all native and external components.
When to use Flutter and when to use React Native development
Because Google supports it, Flutter is a critical React Native alternative to consider even though it was simple to find React developers.
Google cross-platform Mobile Development uses the Dart compiler in contrast to React Native development, which relies on WebView and JavaScript layer and slows down a React Native mobile app.
A built-in rendering engine in Flutter enables for incredibly unique designs, albeit at the expense of bulkier applications. Only native components, some of which may need manual adjustments, are compatible with React Native. A Flutter programme can start in the desktop environment, while a React app must first launch through a web interface.
To assist you in choosing which technologies to include in your IT stack, we’ve created a checklist.
Choose Flutter if:
- You don’t need native functionality entirely for your plan.
- You have a limited timeline and financial capacity.
- You want to write codes faster and release them to the public as soon as you can.
- You anticipate saving money on capital costs by creating a single codebase that is compatible with several platforms.
- You want to create programmes that operate between 60 and 120 frames per second.
- You should run fewer tests and use widgets to modify the ui.
- You wish to expand your current apps by using cross-platform modules.
- Create native apps that are reasonably light.
- You are looking for quick approaches to develop shared APIs.
- Strive to create an application with an asynchronous build and a responsive user interface.
- You are able to commit the necessary time and resources to the project
Young Techies is a company that specializes in creating cross-platform apps. Are you looking for seasoned developers to build a project from scratch then? Please get in touch with us about your project, and we will be happy to help.